|
|
|
|
FOCUS K3D
FOster the Comprehension, adoption and USe of Knowledge intensive
technologies for coding and sharing 3D media content in consolidated
and emerging application communities
http://www.focusk3d.eu
FOCUS K3D is a Coordination Action promoting the comprehension,
adoption and use of knowledge intensive technologies for coding and
sharing 3D media content in application areas that are both consolidated
in the massive use of 3D digital resources (like Biomedicine or Product
Modelling) and emerging (like Gaming or Archaeology). The projects aims
at: - building multi-disciplinary communities of researchers, 3D
content creators and users;
- identifying issues that currently
inhibit a broader user participation in the production of 3D content,
and initiatives acting as catalysts for such a development;
-
promoting and evaluating the results achieved by recent and ongoing
projects to identify promising future developments.
|

|
|
|
Keywords: shape, semantics, knowledge, community.
Duration: March 2008 - February 2010
Funding Organization: European
Commission
Funding Programme: IST Information
Society Technologies - FP7 - Coordination Action
Partners:
- Coordinator: CNR-IMATI-Ge
- CNR-IMATI-Ge - Italy
- CERETETH - Greece
- EPFL - Swiss Federal Institute of
Technology - Switzerland
- FRAUNHOFER - Germany
- INRIA - France
- MIRALab - Switzerland
- SINTEF - Norway
- UU - Utrecht University - The Netherlands
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SHALOM:
SHApe modeLing and reasOning: new Methods and tools
Ricerca Italiana - The SHALOM Project
The objective of SHALOM project is to study innovative methods
for the analysis and synthesis of digital shapes, which constitute the most relevant part of visual media.
A shape is any individual object having a visual appearance which exists in a two or higher dimensional space.
Pictures, sketches, images, 3D objects, videos, animations are examples of shapes. Digital shapes occur and are
used in many different contexts, such as industrial design, biomedical applications, entertainment, environmental monitoring,
cultural heritage, and many more. Because of the evolution in hardware and in software technologies for acquiring
and visualizing shape information and of the increasing number of applications which require more and more advanced
and complex digital shapes, there is a real explosion of models, which cannot be represented with the necessary accuracy
and conciseness nor retrieved from existing archives. The new problems related to this issue require efficient and
effective solutions for both storing and retrieving information as well as for modelling and analysis,
which need transformations among representations, extraction of salient features, reconstruction of complex shapes, etc.
The activities proposed by SHALOM are aimed at answering to the previously described requirements
by integrating complementary research activities done by the three laboratories involved, in order
to propose general solutions to unsolved or partially solved problems.
|

|
|
|
Keywords: shape, modelling, analysis, retrieval.
Duration: July 2006 - June 2009
Funding Organization: FIRB
Funding Programme: International cooperation Italy/Israel
Code: RBIN04HWR8
Partners:
- CNR-IMATI-Ge - Italy;
- DISI - Università di Genova -
Italy;
- Technion CGGC - Israel;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AIM@SHAPE:
Advanced and Innovative Models And Tools
for the development of Semantic-based
systems for Handling, Acquiring, and
Processing knowledge Embedded in
multidimensional digital objects
http://www.aimatshape.net
What are the
common characteristics of shapes? They all
have a geometry, they can be described by
structures (object features and part-whole
decomposition), they have attributes
(colours, textures, names, attached to an
object, its parts and/or its features),
they have a semantics (meaning, purpose),
and they possibly evolve in time (e.g.
shape morphing, animation, video...).
AIM@SHAPE is a Network of
Excellence aimed at coordinating
research on representing, modelling and
processing knowledge related to digital
shapes.
|

|
|
|
Keywords: shape, semantics.
Duration: January 2004 - December
2008
Funding Organization: European
Commission
Funding Programme: IST Information
Society Technologies - Network of
Excellence
Key Action: 2.3.1.7 Semantic-based
knowledge systems
Partners:
- Coordinator: CNR-IMATI-Ge
-
DISI - Università di Genova -
Italy;
- EPFL - Swiss Federal Institute of
Technology - Switzerland;
- IGD - Fraunhofer - Germany;
- INPG - Institut National Polytechnique
de Grenoble - France;
- INRIA - France;
- CERTH - Center for Research and
Technology Hellas - Greece;
- UNIGE - Université de
Genève - Switzerland;
- MPII - Max-Planck-Institut für
Informatik - Germany;
- SINTEF - Norway;
- Technion CGGC - Israel;
- TUD - Darmstadt University of
Technology - Germany;
- UU - Utrecht University - The
Netherlands;
- WIS - Weizmann Institute of Science -
Israel.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Surface Analysis
http://www.ima.ge.cnr.it/ima/personal/CGG/SurfaceAnalysis.html
The Surface
Analysis joint project is aimed at the
exploration of algorithms for the
segmentation, parameterization, and
analysis of complex surfaces. Initially,
it will focus on triangulation of static
surfaces, with the intention to explore
the generalization of the developed
approaches to time-dependent surfaces
models.
|

|
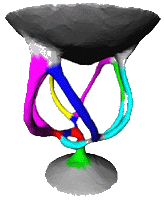
|
|
Keywords: parameterization,
segmentation, compression, analysis of
complex surfaces.
Duration: June 2002 - June 2005
Partners:
- IMATI-GE CNR
- GVU, Georgia Institute of
Technology, Atlanta, USA
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FIORES II: Character
Preservation and Modelling in Aesthetic
and Engineering Design
http://www.fiores.com
FIORES-II aims
at building CAD tools which are capable to
capture and preserve the product aesthetic
character and make it accessible in a
multi criteria approach for styling and
engineering design optimisation. This will
be achieved by reaching the following
objectives:
- Finding a formal structure in
aesthetic properties and terms to
capture the design intent and the
styling character, basing on interviews
and analyses of psychologists.
- Finding a mapping of styling
character descriptions on aesthetic
properties. These properties should be
objectively describable by computable
and measurable parameters.
- Developing methods for the
extraction of aesthetic shape
properties (algorithms).
- Developing methods to optimise the
design due to aesthetic and geometric
respectively engineering
requirements.
IMATI will
contribute in particular to the definition
and formalisation of the aesthetic
properties that contribute to the shape
character and of the relations among
them.
|
|
|
Keywords:CAD, CAS, Aesthetic design,
Design intent, Styling workflow,
Engineering in reverse.
Duration:2000 - 2003
Partners:
-
- University of Kaiserslautern,
Germany (Coordinator)
- Alessi , Italy
- BMW Technik GmbH , Germany
- CAxOPEN product development
technology GmbH , Germany
- Centre de Recherche de Psychologie
Coginitive , France
- Eiger S.L., Spain
- FORMTECH AB, Sweden
- IMATI-GE CNR Italy
- Pôle Universitaire
Léonard de Vinci, France
- Saab Automobile AB, Sweden
- Samtech SA , Belgium
- think3 SPA , Italy
- UDK Utvechling, Sweden
|
|
|
|
|
|
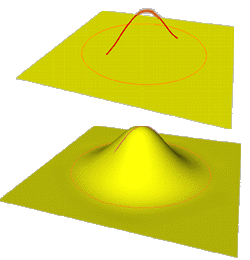
FreeForm Deformation
for Aesthetic and Engineering Design
http://www.ima.ge.cnr.it/ima/personal/FFF/FFDeformation.html
The research
includes the study of deformation methods
for free-form surfaces inside the design
process of products, subjective to
aesthetic and engineering requirements. In
the study of deformation methods the
specification and identification of
geometric features forms the basis of a
free form surface modification process.
The mentioned features designate data
structures, the operators, the properties
of deformation methods that fit into the
requirements and constraints expressed by
the designer.
|
|
|
Keywords:free form modelling, free form
features, surface deformation, industrial
design.
Duration: 2001 - 2003
Partners:
-
- IMATI-GE CNR Italy
- Laboratory 3S- Ecole Nationale
Supérieure d'Hydraulique et de
la Meécanique, Grenoble, France
http://www.3s.hmg.inpg.fr
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shape-based Meshing
Techniques
Depending on
the application, a triangulation can be
treated in order to improve its behavior
under particular circumstances; the
typical example is the Delaunay
Triangulation which usually optimizes the
numerical robustness, however other kinds
of optimization may be more suitable in
different cases. When an application deals
with models of well known shape, for
example, it could be preferable to
maintain some characteristics of the
represented object rather than optimize
everything using the Delaunay criterion;
moreover, these meaningful
characteristics, or features, can be
exploited for a wide range of goals, like
high-level description of the shape, model
compression, construction of levels of
detail for multiresolution and so on.
Shape reasoning can give an extensive help
for the development of a comprehensive
conceptual model for the representation of
semantic and topological properties of
structural surface feature classes, and
the automatic feature extraction from
various data structures (grid, TIN, lines,
etc.). Such tools can be used in order to
improve the polygonization process and to
construct more semantically detailed
meshes.
The research topics which we planned to
tackle in this research agreement will
cover:
- Shape modeling and analysis
- Shape-based Polygonization
Techniques
- Error evaluation for polygonization
processes
- Multiple representation of 3D
surfaces
|

|
|
Keywords: Shape modeling and
analysis,Shape-based Polygonization
Techniques Error evaluation for
polygonization processes, Multiple
representation of 3D surfaces.
Duration: 2000 - 2003
Partners:
|
|
|
|
|
|
FIORES: Formalization
and Integration of an Optimized Reverse
Engineering Styling workflow
http://rkk.mv.uni-kl.de/FIORES/home.html
Obiettivo di
questo progetto è l'introduzione di
soluzioni innovative nel processo di
progettazione assistita da calcolatore per
quanto riguarda la fase di disegno
estetico. A questo scopo, vengono proposti
una nuova interfaccia utente e un nuovo
insieme di strumenti per verificare la
qualità morfologica del disegno, al
fine di agevolare l'accettazione degli
strumenti informatici di progettazione da
parte dello stilista. Viene inoltre
fornita all'utente la possibilità
di specificare in maniera oggettiva le
proprietà della forma del prodotto,
in modo da potenziare le tecniche di
Reverse Engineering per la costruzione di
un modello con le caratteristiche
volute.
|

|
|
Keywords: Computer-Aided Styling,
Engineering in reverse, Feature-based
modeling, working with properties.
Duration: 1997 - 2000
Partners:
-
- University of Kaiserslautern,
Germany (Coordinator)
- BMW AG, Munchen, Germany
- IMATI-GE CNR
- PININFARINA Studi e Ricerche,
Torino, Italy
- MATRA DATAVISION, Paris,
France
- SAMTECH SA, Liège,
Belgium
- Centro Internationel de
Métodos Numéricos
(CIMNE), Barcelona, Spain
- Eiger S.L., Barcelona, Spain
- Taurus Electrodomesticos, Oliana,
Spain
- FORMTECH AB, Torslanda, Sweden
- Saab Automobile AB, Trollhattan,
Sweden
- UDK Utveckling, Savedalen,
Sweden
|
|
|
|
|
|
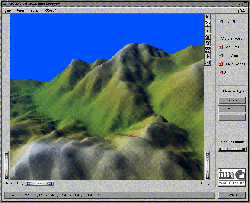
High-Quality Digital
Terrain Modelling
The project
addresses the frequent requirement of
scientists, engineers, decision makers, to
access, process and visualize vast amount
of surface data. Moreover, special care
has to be devoted to uncertainty handling:
traditional modelling techniques are
unable to explicitly represent uncertainty
which may derive from the surface sampling
process, and are also insufficient to
support the users with quality assessment
tools for validating the surface model and
related analysis processes. In the
described scenario, the IMA-CNR will
develop for the Monolith co. an advanced
system for modelling and processing
surface data which integrates traditional
techniques (e.g. triangulation, grids or
contours) with tools for the analysis of
shape features (e.g. critical point and
line extraction, curvature analysis).
Shape features are essential for defining
high-level representations of surface data
which capture the main structure of
surfaces (conceptual modelling). Special
emphasis will be put on the definition of
simplification and compression tools for
both for data and models (e.g. decimation,
vertex or edge collapse, fuzzy-like data
clustering).
|
|
|
Keywords: Digital terrain modelling,
data simplification, topographic feature
extraction, conceptual modelling.
Duration: 1998-2001
Partners:
-
- IMATI-GE CNR
- Monolith co. Ltd., Tokyo
|
|
|
|
|
|
Analysis of Digital
Terrain Model for the detection of
topographic features of interest for the
environment protection
The objective
of the project is to study methods of
geometric reasoning for the analysis of
digital terrain models to detect
morphological information of interest in
the environment study. The main aim is to
construct a computational module to
automatically detect relevant
topographical features from the ambient
point of view, such as: mountain mounts,
mountains and gutters of rivers. The
modules is integrated in the Geographic
Information System SPRING developed by the
Brazilian team.
|
|
|
Keywords: Digital terrain model,
Surface characterisation, Geographic
Information System.
Duration: 2001
Partners:
-
- INPE - Instituto Nacional de
Pesquisas Espaciais, Sao Josè
dos Campos, Brazil
- IMATI-GE CNR
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mediterraneo: Enhancing
Product Development Through Physical
prototype Rapid e-Delivery
The primary
aim of the network is to increase the
awareness of e-business advantages for
product development, taking advantage of
the existing technologies independently of
their physical location, thus allowing a
better exploitation of production
capabilities and collaboration of remote
countries. The network will share the
parteners' competencies in order to
increase the knowledge in
- distributed collaboration
- shape recognition
- rapid prototyping technologies and
requirements
and to
coordinate current research activities of
the partners to enforce research
collaboration.
|
|
|
Keywords: geometric modelling,
distributed product development.
Duration: 2001 - 2002
Partners:
-
- IMATI-GE CNR
(Coordinator)
- Department of Manufacturing
EngineeringUniversity of Malta
(Coordinator)
- Technimold S.r.l.V. Genova,
Italy
- FhG-IPA: Fraunhofer-Institut fuer
Produktionstechnik und Automatisierung
Manufacturing Engineering and
Automation Technische
Informationsverarbeitung Stuttgart -
Germany
|
|
|
|
|
|
European Project ESPRIT
"COWORK: COncurrent project development IT
tools for small-medium enterprises
netWORKs"
http://www.tekniker.es/cowork
The COWORK
project is targeted at developing a new
software tool enabling Small and Medium
Enterprises (SMEs), working in the
mechanical sector, to cooperate in a
distributed engineering environment to
dramatically save time and reduce products
engineering costs. This objective may be
reached by encouraging SMEs enterprises to
systematically apply Concurrent
Engineering and Co-design techniques, duly
supported by a new specially-conceived
software.
|

|
|
Keywords: Concurrent Engineering,
Co-design.
Duration: 1997-2000
Partners:
-
- FUNDACION TEKNIKER Spain
(Coordinator)
- FATRONIK SYSTEM Spain
- Tkm XXI Spain
- GORATU Spain
- DEMOCENTER Italy
- CNR-IMATI Genova
- ZGDV Germany
- Fraunhofer IGD Germany
- PROSTEP Germany
- AMCO VEBA Italy
- ELLETTARI Italy
- TECNOMET Italy
- SPEED AUTOMAZIONE
- RMT Germania
|
|
|
|
|
|
ARION: An Advanced
Lightweight Architecture for Accessing
Scientific Collections
http://www.arion-dl.org
ARION is
aiming to provide a new generation of
Digital Library services for the searching
and retrieval of digital scientific
collections that reside within research
and consultancy organisations. These
collections contain data, programs and
tools in various scientific areas and
incorporate applications of different
domains of knowledge. ARION advances the
findings of previous studies in areas,
such as, management of networked
scientific repositories and metacomputing.
It consolidates the work of international
interoperability standard development to
provide a system that is complementary to
established scientific practices in these
organisations. ARION will be a federated
open system and will be developed in
association with national data providers,
scientific researchers and SME’s to
ensure that the project meets their
needs.
|

|
|
Keywords: Digital Scientific
Library.
Duration: 2001-2003
Partners:
- Foundation for Research and
Technology, Institute of Computer
Science, Heraklion, Greece
(Coordinator)
- HR Wallingford Ltd, Wallingford,
Great Britain
- Joint Research Center, Space
Application Center, Marine Environment
Unit, Ispra, Italy
- National Technical University of
Athens,Greece
- Oceanographic Company of Norway
ASA, Trondheim, Norway
- University of Crete, Heraklion,
Greece
- IMATI-GE CNR
|
|
|
|
|