|
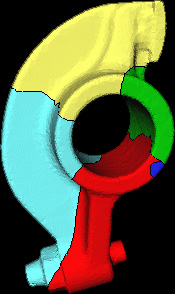
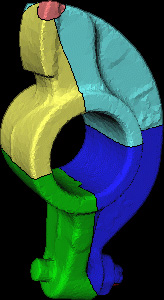
Local parameterization of arbitrary triangle meshes.
We developed
a novel approach to the parameterization of triangle meshes
representing 2-manifolds with an arbitrary genus. A topology-based
decomposition of the shape is computed and used to segment the shape
into primitives, which define a chart decomposition of the mesh. Then,
each chart is parameterized using an extension of the barycentric
coordinates method. The charts are all 0-genus and can be of three
types only, depending on the number of boundary components. The chart
decomposition and the parameterization are used to define a shape graph
where each node represents one primitive and the arcs code the
adjacency relationships between the primitives. Conical and cylindrical
primitives are coded together with their skeletal lines that are
computed from and aligned with their parameterization. The application
of the parameterization approach to remeshing guarantees that
extraordinary vertices are localized only where two patches share a
boundary and they are not scattered on the whole surface.
Patanè
G., Spagnuolo M., Falcidieno B. Para-Graph: Graph-Based
Parameterization of Triangle Meshes with Arbitrary Genus. In:
Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 23 (4) pp. 783-797. Blackwell Publishing,
2004. [PDF]
|
  |
|
Global
Parameterization of Bordered Triangle meshes with arbitrary genus
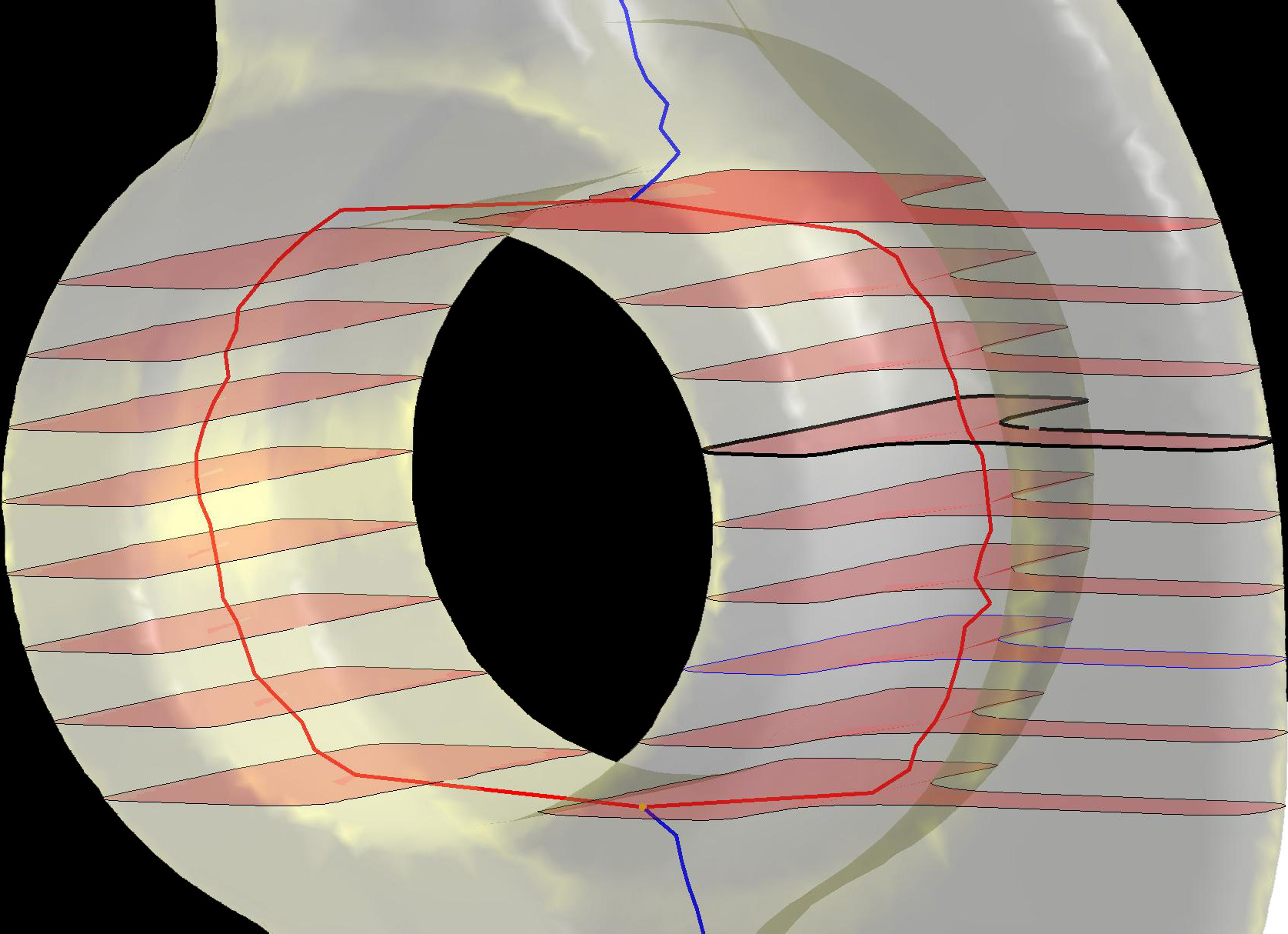
The
set of cut graphs for a given triangle mesh M with an arbitrary genus
depends on the underlining topology and the selection of a specific one
should be guided by the surface geometry and targeted
applications. The influence of the mesh connectivity on the cut graph
search affects previous work due to the use of algorithms based on mesh
traversal techniques for the evaluation of the geodesic metric. Our
solution is to search a cut graph made of the iso-contours of a fair
function f: M->R and to work in a planar domain where geodesic
curves are defined by line segments whose counterparts on M, with
respect to an appropriate diffeomorphism, give smooth approximations of
geodesic paths. The emphasis of the paper is on the definition of a
simple method for finding a family of cut graphs of M and guided by
several criteria which spread from the global parameterization (e.g.,
minimal length, minimization of the parameterization distortion, or
interpolation of points as required by remeshing and texture mapping)
to the calculation of polygonal schemes for surface classification. The
proposed approach finds a cut graph of a
closed or bordered triangle mesh M with n vertices in O(n) time if M
has 0-genus, and O(nlog(n)) time if g>0; finally, the associated
polygonal schema is reduced if g=0 and with a constant number of
redundant edges otherwise.
Patanè G., Spagnuolo M., Falcidieno B. Families
of cut-graphs for bordered meshes with arbitrary genus . In:
Graphical Modeals,
2006.To appear. [PDF]
|
 |

